Addressing Climate Change
Promoting initiatives for carbon neutrality
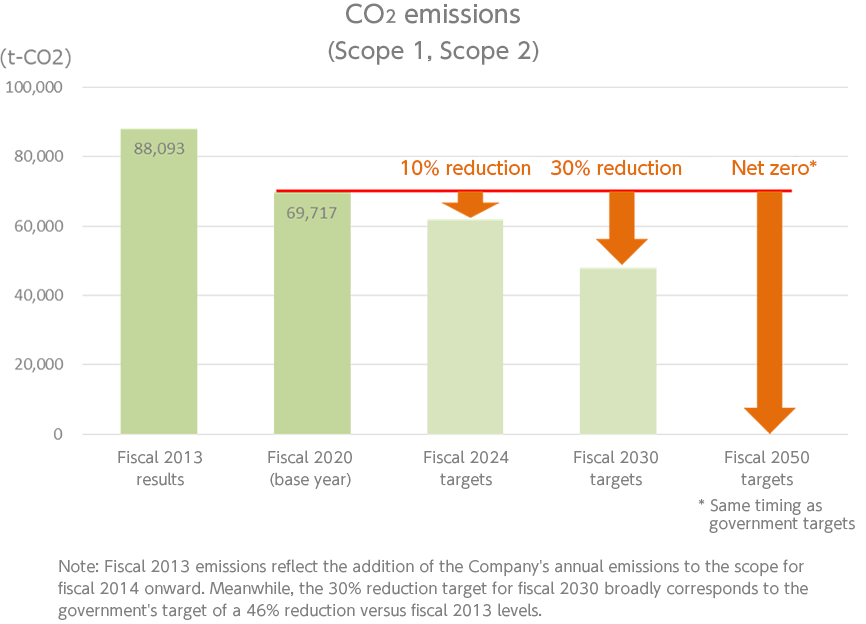
We carry out initiatives to achieve the goals for CO2 reduction we set with the CO2 emissions from Scope 1 + 2 of FY2020 as a point of reference: a short-term target of 10% reduction by the end of FY2024, and a mid-term target of 30% reduction by the end of FY2030.
Information Disclosure Based on the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosure (TCFD) recommendations

The Alfresa Group views climate change as a major issue that impacts sustainability management.
Based on the declarations*1 of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD*2), Alfresa advances initiatives within the following framework.
*1 Alfresa group supports the TCFD recommendations.
*2 The TCFD was established in 2015 by the Financial Stability Board, an international organization. The TCFD proposes methods to evaluate companies' business risks and opportunities due to climate change and encourages them to disclose information about the financial impact of such risks and opportunities.
Corporate governance (climate governance system)
The Alfresa Group is addressing climate change as one of its aims in the Alfresa Group's Environmental Policy.
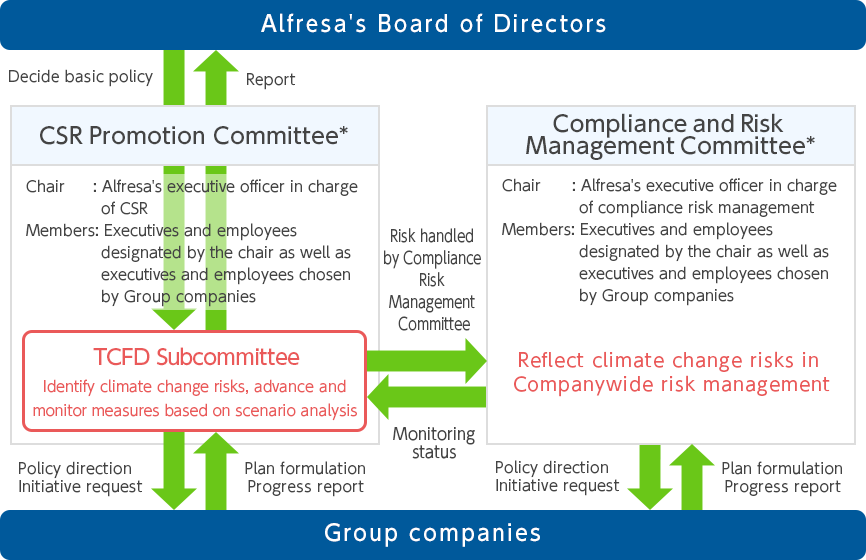
The Group set up the TCFD Subcommittee under the Group Sustainability Promotion Committee in May 2022 for the purpose of improving information disclosure related to climate change.
The TCFD Subcommittee works closely with the Compliance and Risk Management Committee, which oversees risk management for the entire Group, to identify risks and opportunities related to climate change, evaluate their importance, and advance and monitor countermeasures.
The content of and the progress made by these measures are reported to the Group Sustainability Promotion Committee twice a year, with reports subsequently submitted to the Board of Directors.
Our stance on addressing climate change is reflected in Group Management Policies in the Mid-term Management Plan, and we advance initiatives to address climate change through business activities.
* The Group Sustainability Promotion Committee and the Compliance and Risk Management Committee are advisory bodies to the Board of Directors.
Roles and Systems
1Role of TCFD Subcommittee
- Identify risks and opportunities, analyze scenarios
- Evaluate importance
- Advance specific measures (work with Group Sustainability Promotion Committee and Compliance and Risk Management Committee)
- Monitor progress (work with Group Sustainability Promotion Committee and Compliance and Risk Management Committee)
- Information disclosure
2Climate change risks and promotion and monitoring system
Group Sustainability Promotion Committee (TCFD Subcommittee)
Mainly in charge of transitional risks and opportunities
Compliance and Risk Management Committee
Mainly in charge of physical risks
Strategy
In fiscal 2021, the year ended March 31, 2022, Alfresa analyzed scenarios to evaluate the impact of climate change on Groupwide operations. Management conducted interviews in each business segment and, based on the following two possible scenarios, identified risks and opportunities in each business, thereafter classifying them in TCFD categories along short-term, medium-term, and long-term time frames. The magnitude of their financial impact was qualitatively evaluated in five stages, and countermeasures were examined based on the degree of importance.
Alfresa views climate change as a medium- to long-term management issue and thus reflects it in its business strategies. Of the identified risks and opportunities, the following items are considered highly important at the Companywide level.
| Possible scenarios |
1.5℃ scenario
Maximum impact from transition to carbon neutrality * Referenced third-party scenarios: International Energy Agency's (IEA) Net Zero by 2050 Scenario / SSP1-2.6 Scenario, RCP 2.6 Scenario |
|---|---|
|
4℃ scenario
Maximum impact from climate change without transition to carbon neutrality * Referenced third-party scenarios: SSP5-8.5 Scenario, RCP 8.5 Scenario |
| Timeframe | Timeframe | Reason for adoption | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short term | Until 2025 | End of 2022 -24 Mid-term Management Plan | |
| Medium term | Until 2030 or so | Outlook for next 10 years or so | |
| Long term | Until 2040 or so | Outlook for next 20 years or so | |
| Very long term | Until 2050 or so | Japanese government's carbon-neutral target timeline |
Major risks and opportunities in 1.5℃ scenario
| Category | Outline of possible scenarios | Business risks and opportunities | Details of risks and opportunities | Timeframe | Strategic response to risks and opportunities | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government policies and regulations |
2030: $130/t-CO2 2050: $250/t-CO2 |
Increase in costs to accelerate reductions in GHG emissions | Risks |
|
Short term |
|
| Rise in costs from introduction of carbon pricing | Risks |
|
||||
| Technologies |
|
Opportunities from efficiency gains in transportation | Opportunities |
|
Short term |
|
| Markets |
|
Rise in electricity prices | Risks |
|
Medium term |
|
|
Increase in naphtha prices | Risks |
|
Long term | ||
| Reputation |
|
Decline in trust of stakeholders due to delays in addressing climate change | Opportunities Risks |
|
Short term |
|
Major risks and opportunities in 4℃ scenario
| Category | Outline of possible scenarios | Business risks and opportunities | Details of risks and opportunities | Time frame | Strategic response to risks and opportunities | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Markets |
|
Increase in crude oil prices | Risks |
|
Medium term |
|
| Acute climate change impact |
|
Impact on bases from wind and water damage | Risks |
|
Short term |
|
| Supply chain disruptions due to wind and water damage | Risks |
|
Short term |
|
||
| Chronic climate change impact |
|
Increase in infectious diseases | Opportunities Risks |
|
Medium term |
|
|
Temperature management and higher air-conditioning costs | Risks |
|
Medium term |
|
|
In addition to the aforementioned major Companywide risks and opportunities, Alfresa has identified major risks and opportunities within each business segment. In the medical-related business, one risk is earnings deterioration in the pharmacy business due to heat waves, while stronger demand for online and door-to-door sales due to heat waves represents an opportunity. In the manufacturing business, one risk pertains to the impact on coastal plants from rising sea levels.
Risk management (process)
|
|
|---|
Indicators and targets
The Alfresa Group has set the target of net-zero CO2 emissions by fiscal 2050, as CO2 emissions are a key indicator related to climate change.
Using fiscal 2020 CO2 emissions (Scope 1 and Scope 2) as a baseline, the Alfresa Group has set targets to reduce emissions by 10% by the end of fiscal 2024 as a short-term objective and by 30% by the end of fiscal 2030 as a medium-term objective.
The Group Sustainability Promotion Committee evaluates measures and policies for using renewable energy and switching to environmentally friendly vehicles, evaluates and reports on the activities of each Group company, and reports its findings to the representative director and Board of Directors. Fiscal 2021 CO2 emissions (Scope 1 and Scope 2) amounted to 70,420 t-CO2.
* Please also refer to the Alfresa Group ESG Data for more information about energy use and CO2 emissions.